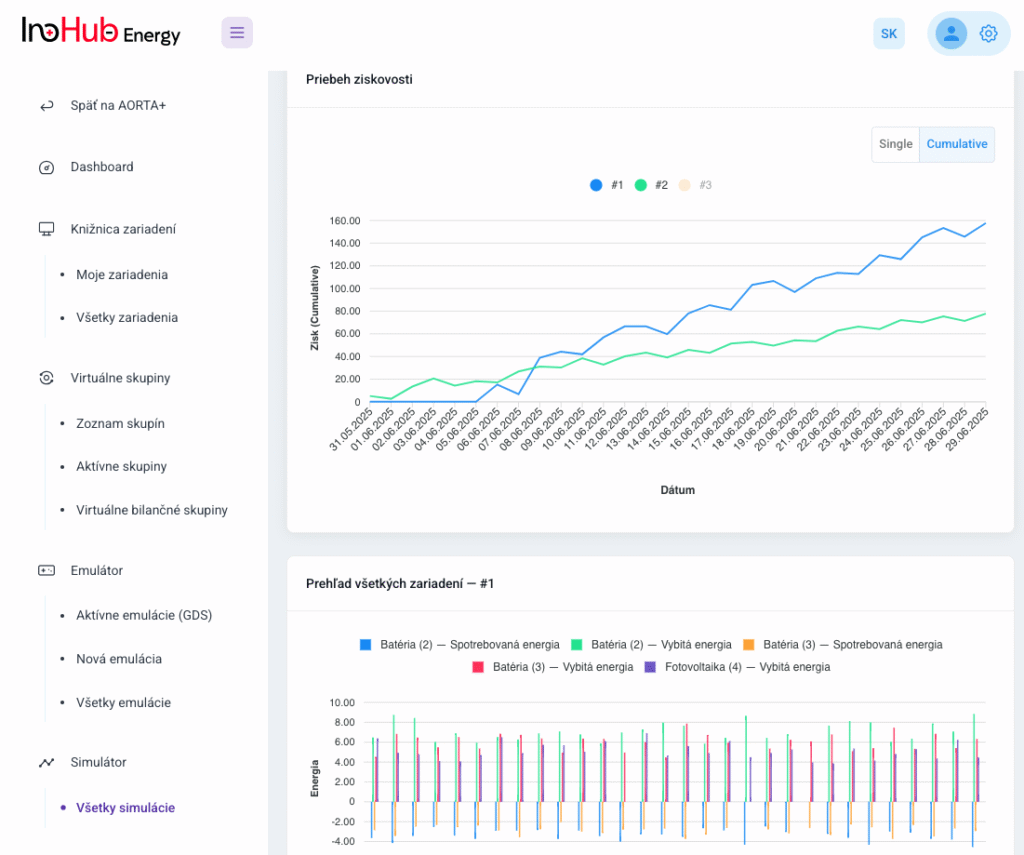
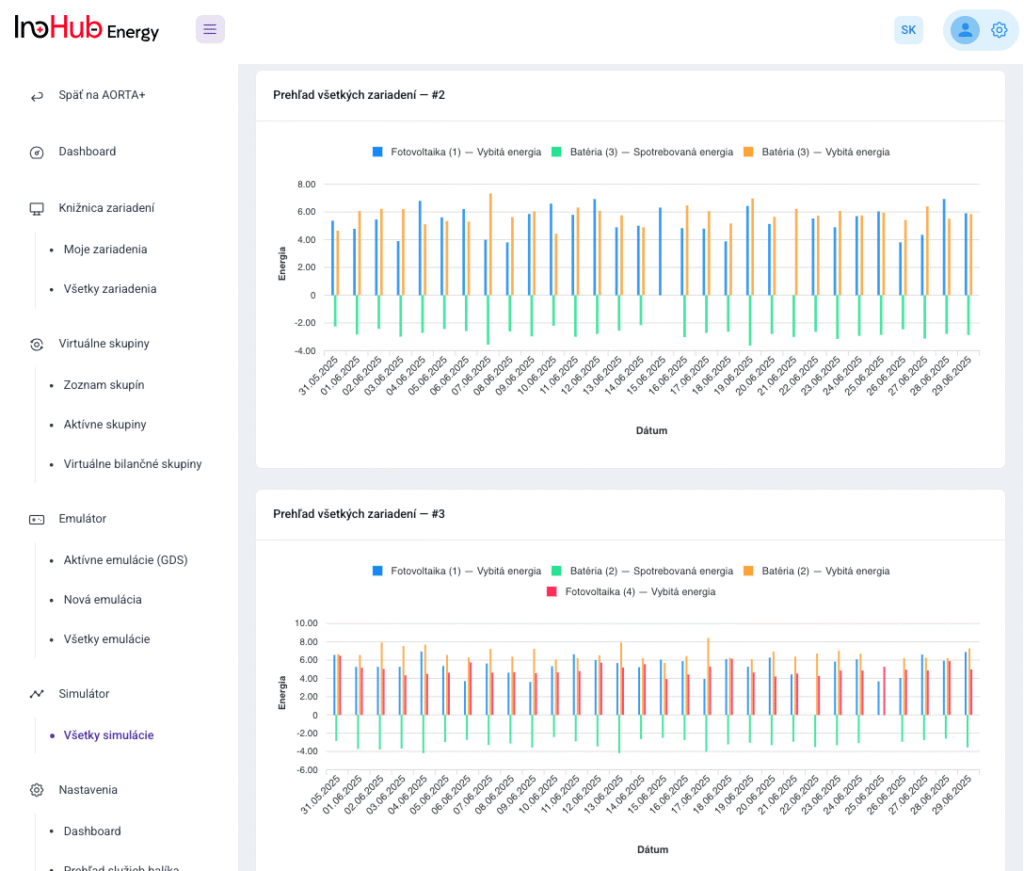
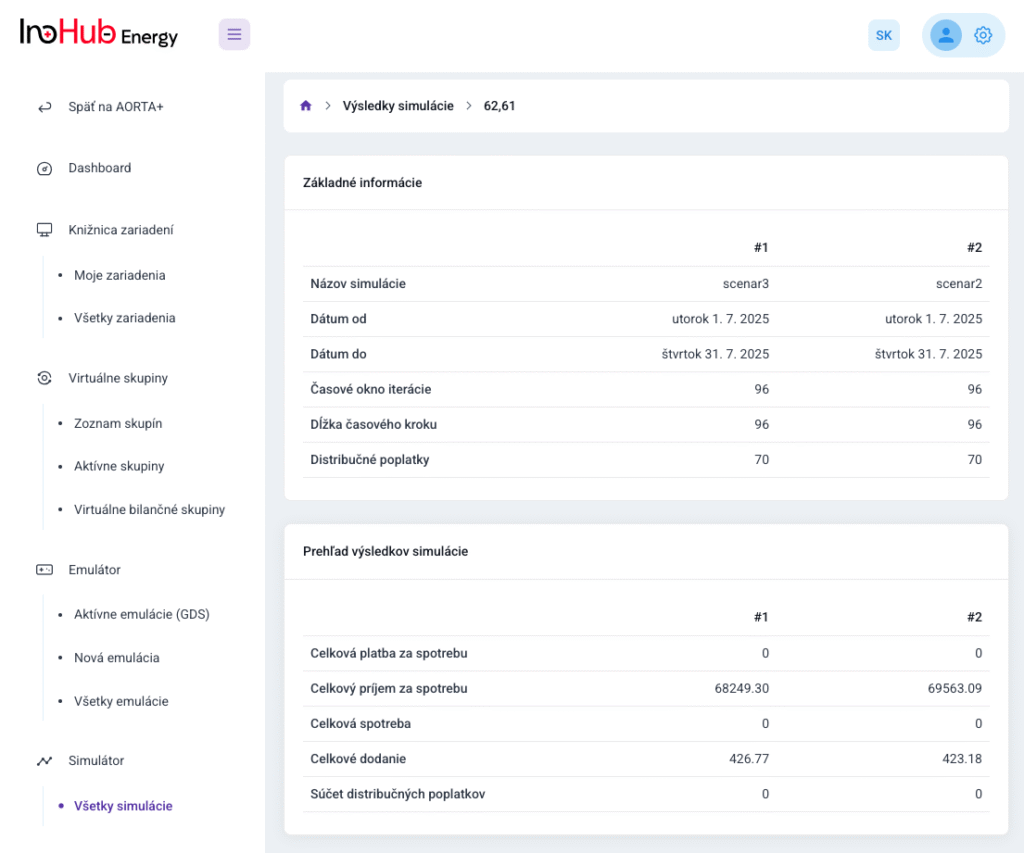
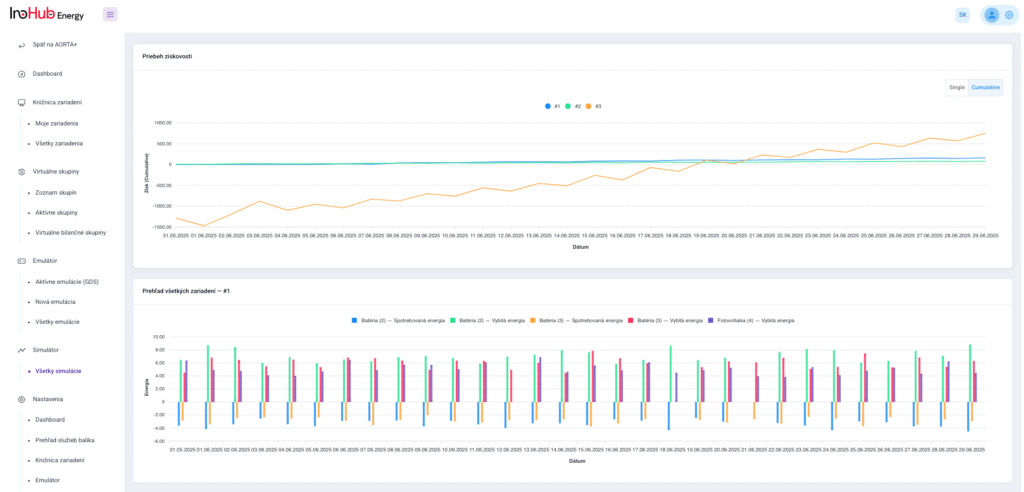
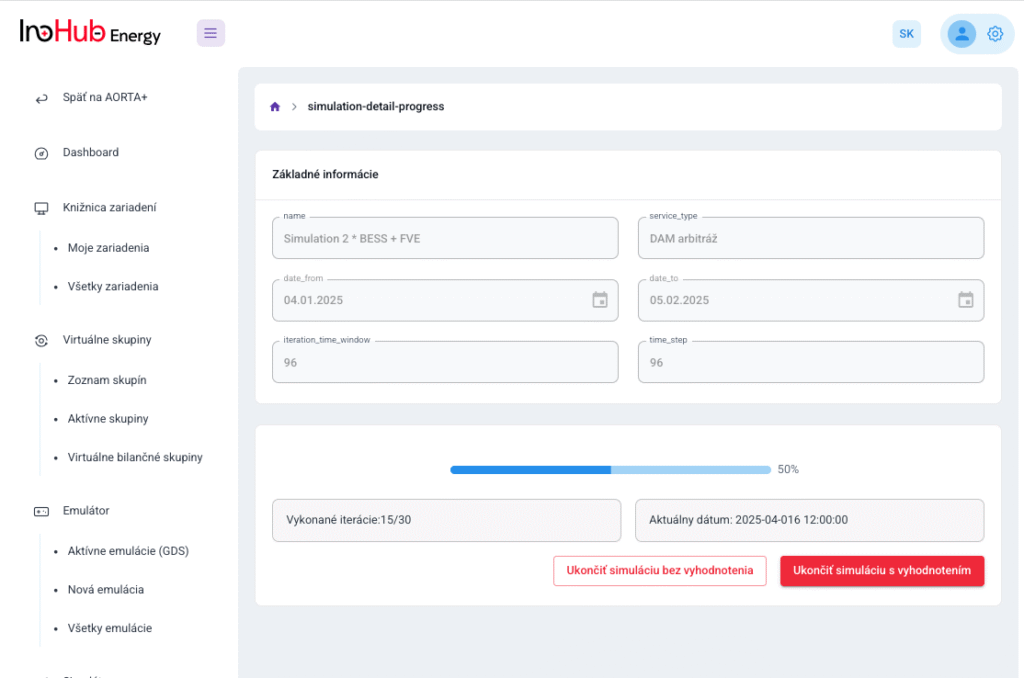
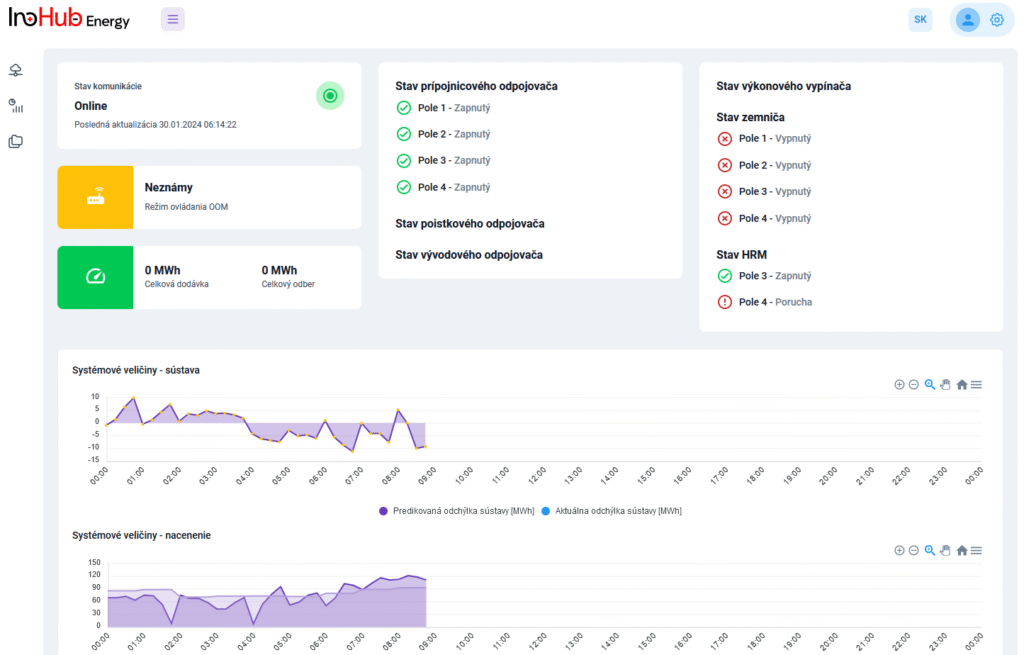
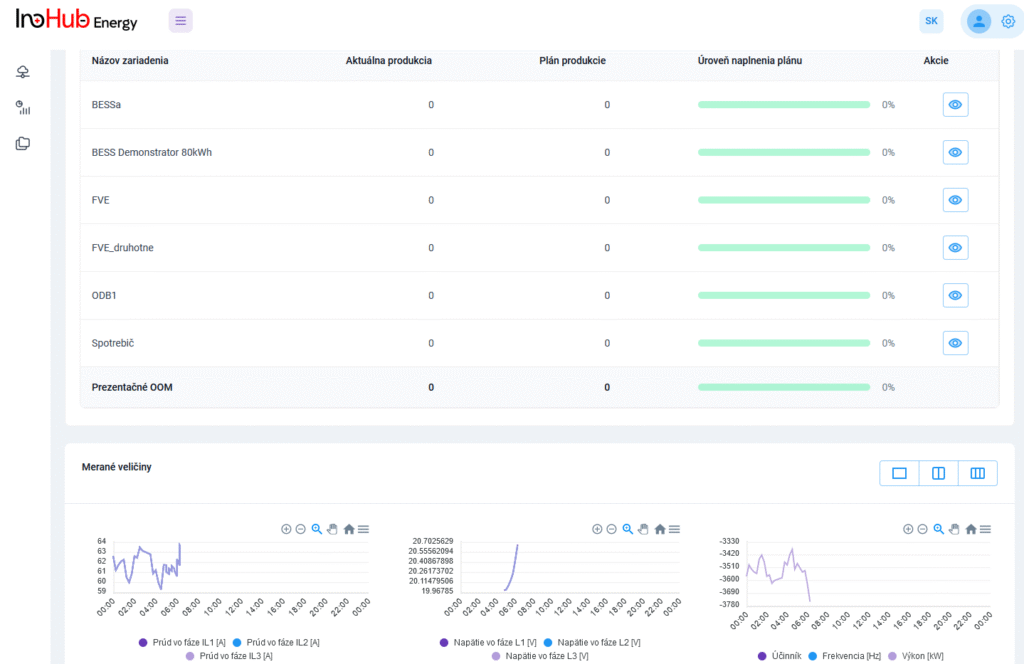
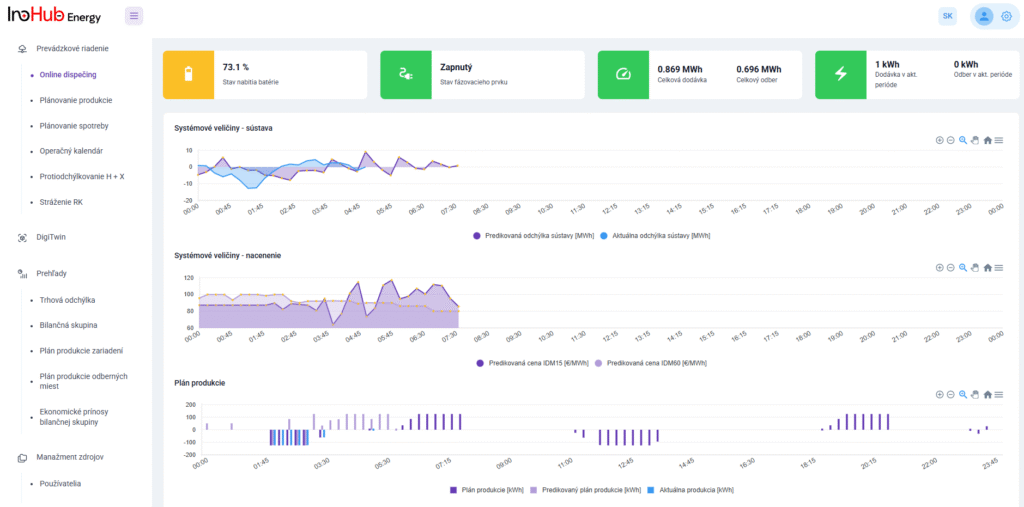
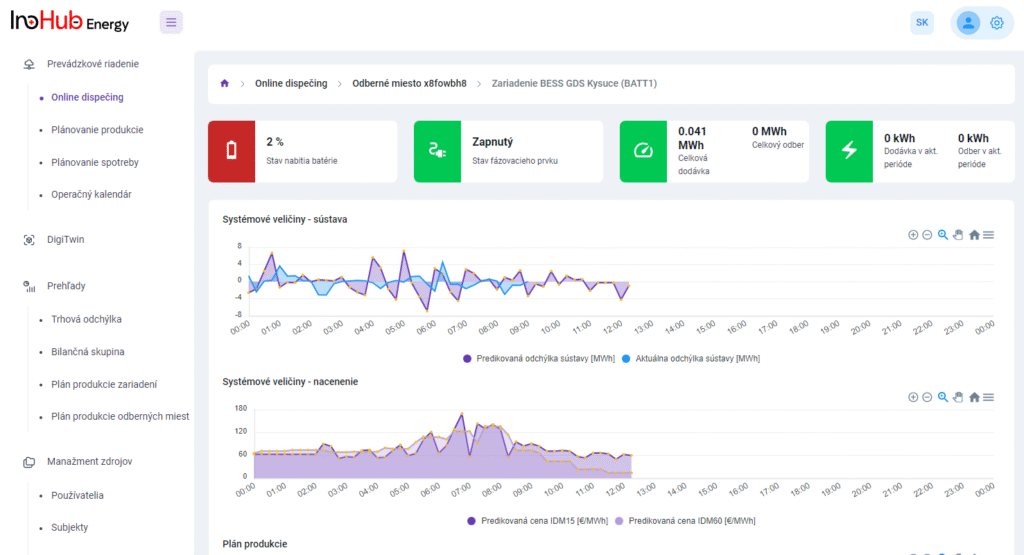
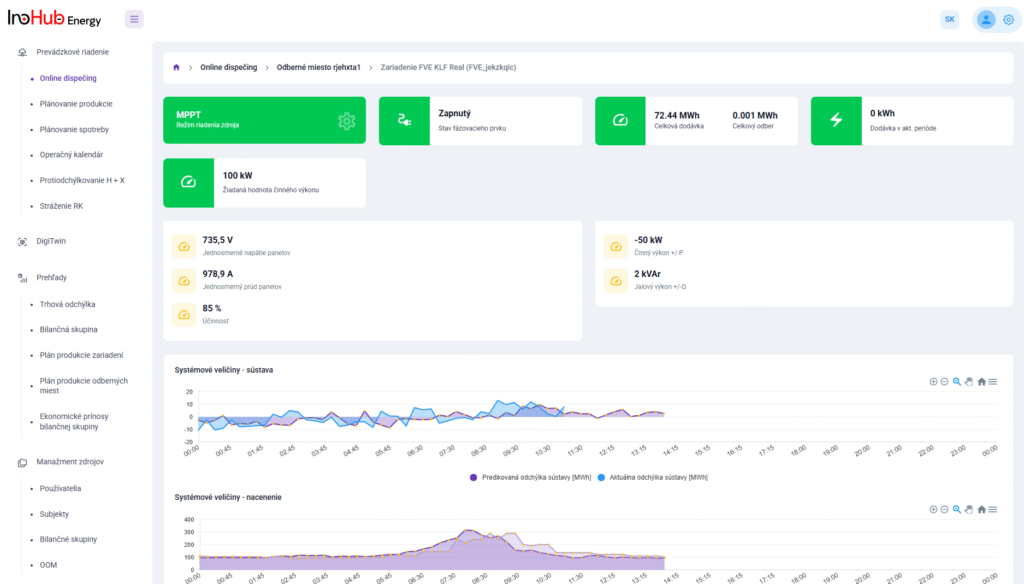
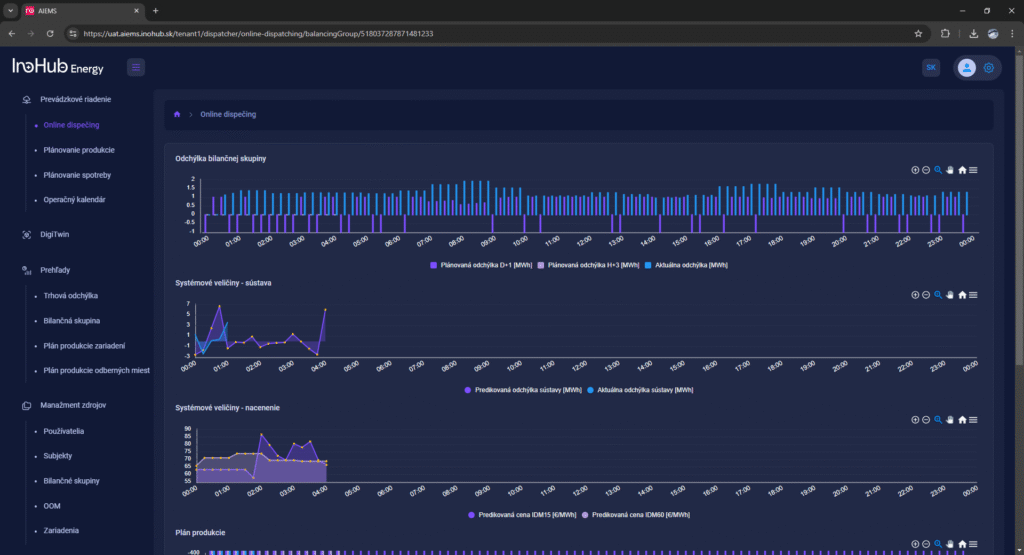
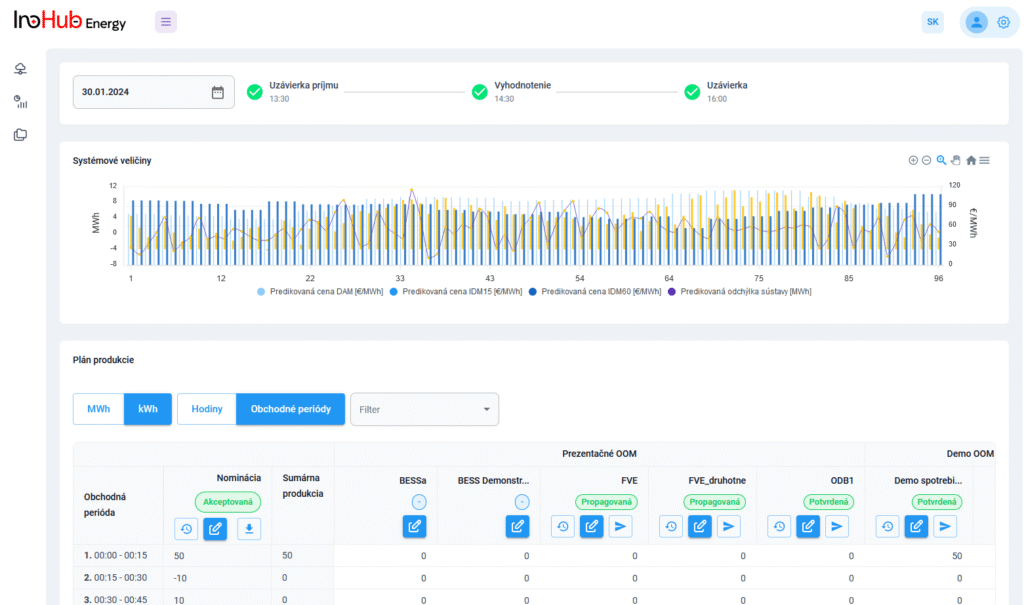
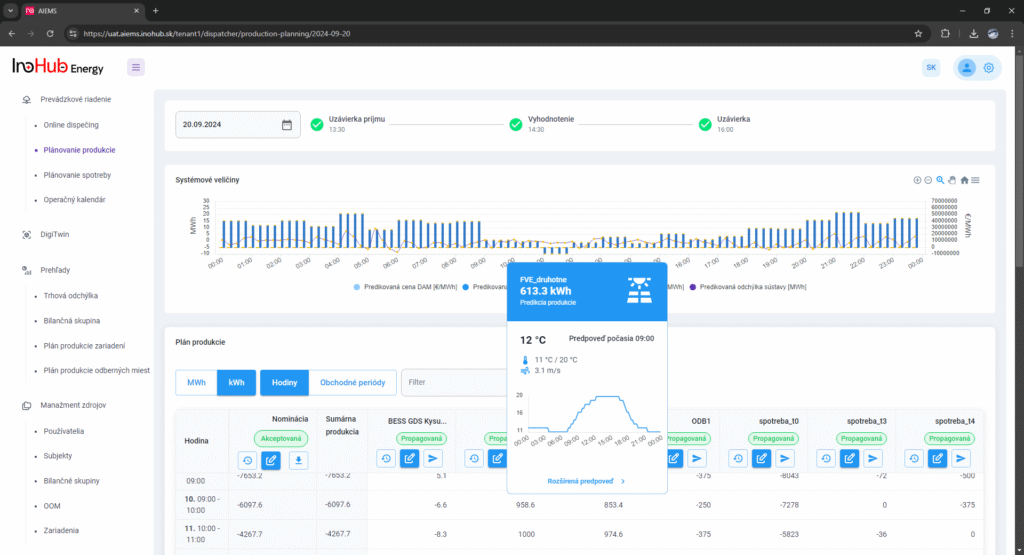
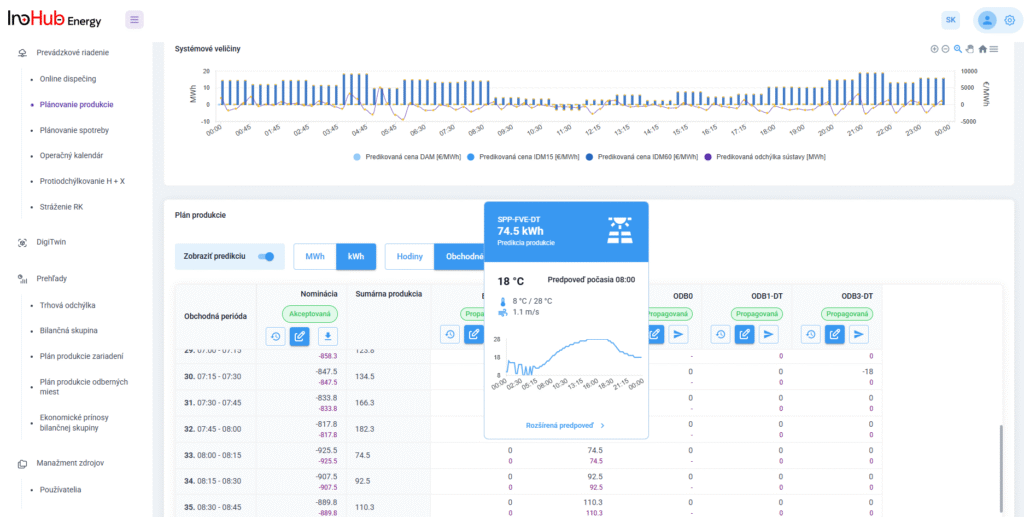
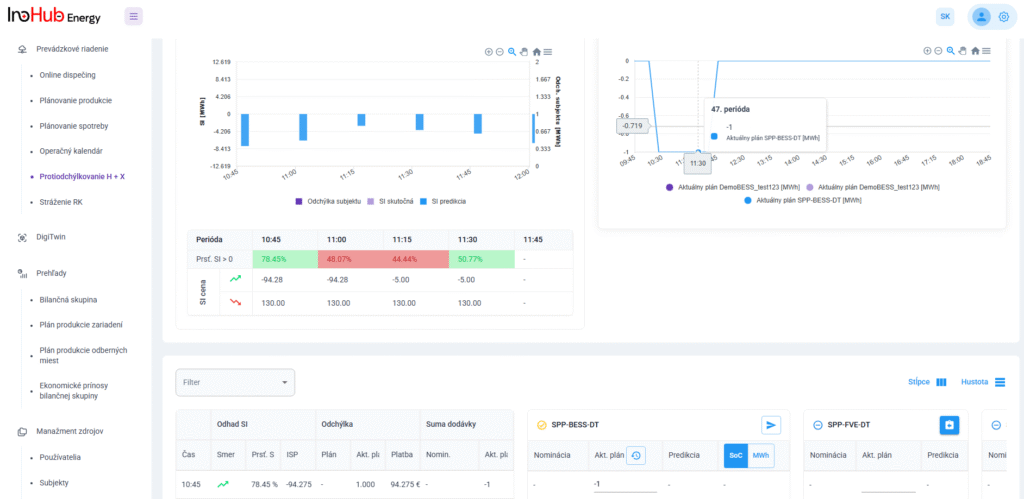
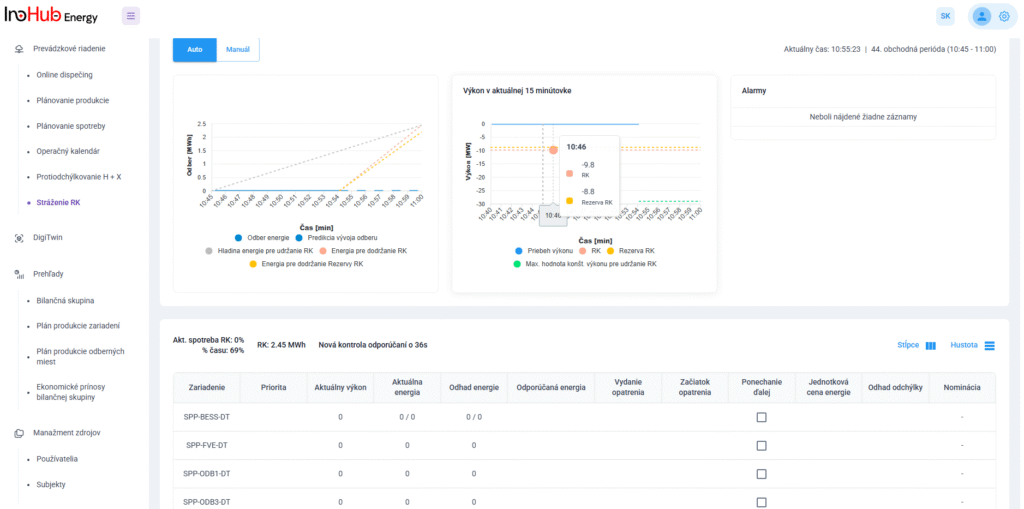
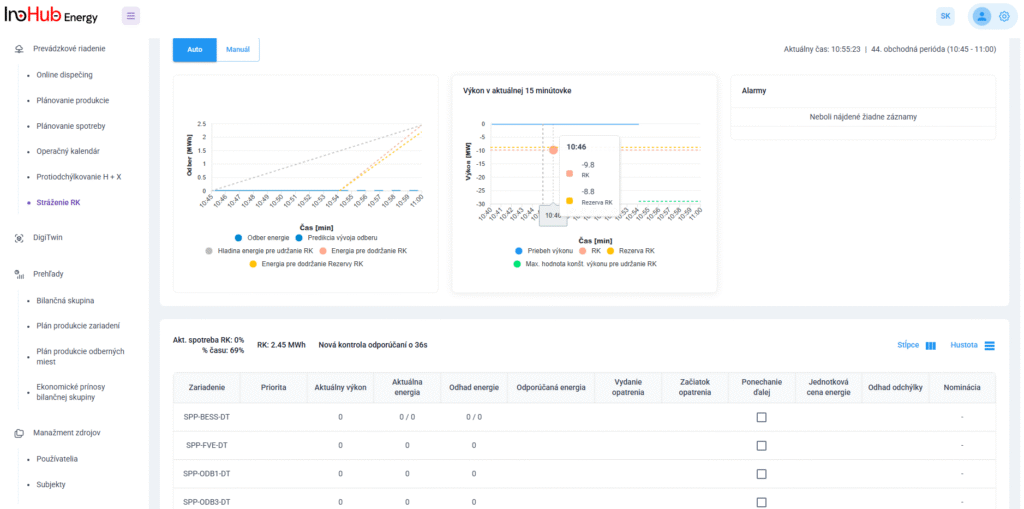
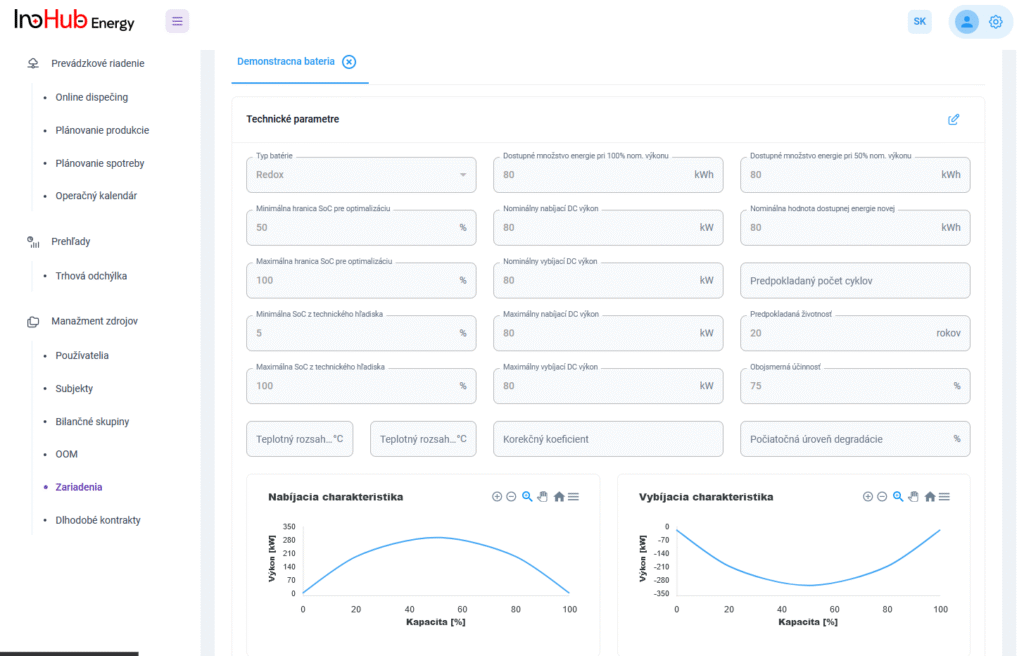
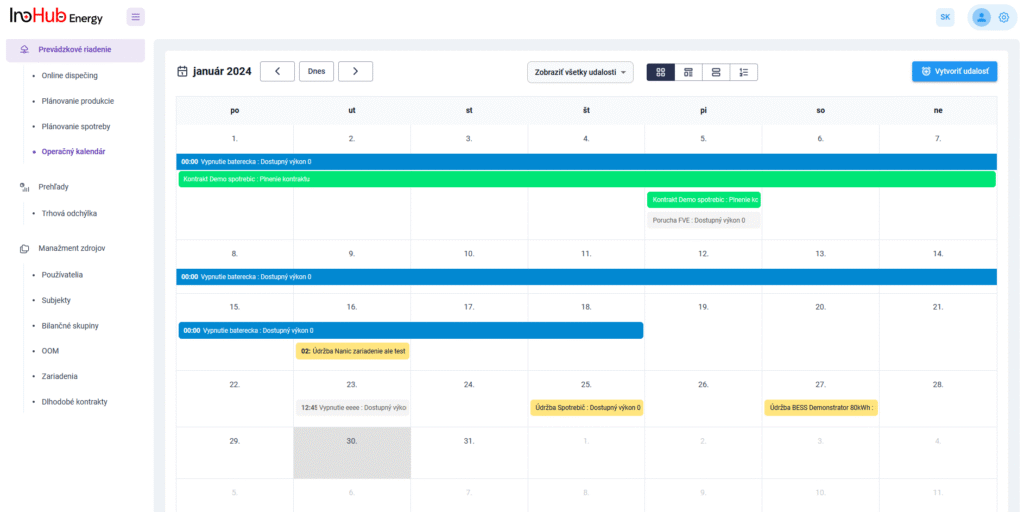
Jednou z hlavných úloh tímu R&D je výskum a optimalizácia nových komponentov batérií zameraná na zníženie nákladov a zvýšenie výkonu z hľadiska životnosti, hustoty energie a teplotného rozsahu.
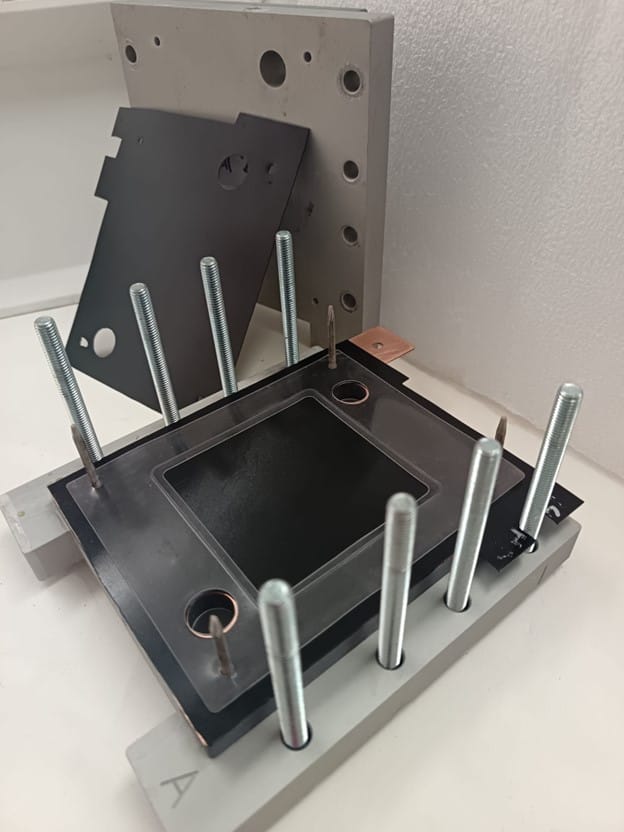
Medzi rôznymi skúmanými témami – ako sú nové organické elektrolyty a alternatívne iónomeničové membrány – má výroba extrudovaných bipolárnych dosiek veľký význam. Dôvodom je potenciál znížiť ich náklady až o 90 % elimináciou používania perfluórovaných polymérov pri paralelnom zvyšovaní ich trvanlivosti.
V tejto súvislosti bola nadviazaná spolupráca s Research Institutes of Sweden (RISE) a spoločnosťou INO-HUB Energy s cieľom vyvinúť extrudované bipolárne dosky. Väčšina komerčných bipolárnych dosiek sa v súčasnosti spolieha na vysoký podiel vodivých materiálov zmiešaných s fluórovanými polymérmi. Nadmerné používanie vodivých materiálov môže negatívne ovplyvniť dlhodobú stabilitu dosiek, pretože sú náchylné na oxidáciu. Na vyriešenie tohto problému je jedným z našich kľúčových prístupov zníženie množstva vodivého materiálu a jeho zmiešanie s nefluórovanými polymérmi. Rôzne základné polyméry, vodivé materiály a kompozity budú hodnotené prostredníctvom ex-situ aj in-situ experimentov, aby sa preukázala ich použiteľnosť v RFB.
POĎAKOVANIE:
Táto práca bola podporená projektom: IPCEI_IE_FLOW_BESS_012021_2. fáza